Define Counting Cards
Latest News
|
| Suggested Tip!Read Books New WaysDoes it feel like you’ve read the same story 100 times? Read it a new way: Ask the child questions about what they think will happen next and encourage them to tell you what they see in the illustrations.Learn more > |
Card counting (Noun) A strategy, in pontoon or blackjack, in which a player keeps a mental tally of the cards played in order to calculate the probability of certain cards being dealt and therefore obtain an advantage. Freebase (0.00 / 0 votes)Rate this definition. In addition, the report recommended that the FDA respond to requests to define terms such as 'low,' 'reduced,' and 'free' carbohydrates as well as provide guidance on use of the term 'net carbs.'
Card counters know that before we bet or play using a balanced strategy,we must adjust the running count by the un-dealt cards. That is, convertthe running count into a true count. Most explanations of true count calculationsimply say that the running count is divided by the number of remainingdecks in the shoe. Blackjack card counting books generally provide a simpleexample, like a running count of +6 divided by three remaining decks yieldsa true count of +2 — and they leave it at that. As a result manyquestions remain. The attempt here is to answer some of these questions.
What is the true count divisor?
When using the Hi-Lo card counting strategy, we divide by the numberof remaining decks. But this is not true of all strategies. For example:
- Revere Point Count and Hi-Lo Lite divide by remaining half-decks.
- The 1998 version of Zen divides by quarter-decks remaining. The originalZen divided by full-decks.
- The Mentor card counting strategy essentially divides by the numberof double-decks remaining. More on this later.
Generally, there is not much difference in overall effectiveness. However,if you are not using fractional true counts for betting, there is a performancepenalty for using half-decks in a level 1 strategy or quarter-decks ina level 2 strategy.

How are non-integer results handled?
Suppose we have a running count of +3 and 2 remaining decks. 3/2=1.5.However, nearly all counters use integers for betting and indexes. Thereexist four methods of converting to integers:
- Truncate – For positive numbers,round down and for negative numbers round up. This is the method usedin the 1994 and later editions of Professional Blackjack. 1.5is rounded down to 1. -1.5 is rounded up to -1.
- Floor – Numbers are always roundeddown. This is the method used in the early versions of ProfessionalBlackjack. 1.5 is rounded down to 1. -1.5 is rounded down to -2.This is the most popular method used now.
- Round – After the True Count division,the result is rounded to the nearest integer. If the number is exactlybetween two integers, it is rounded up. 1.5 is rounded up to 2. -1.5is rounded up to -1. This method is also common.
- Statistical Round – After the TrueCount division, the result is rounded to the nearest integer. If thenumber is exactly between two integers, it is rounded to the nearesteven number. 1.5 is rounded up to 2. -1.5 is rounded down to -2.
Flooring and rounding are nearly equal in performance. Truncating isslightly inferior as it results in a very large percentage of true countsof zero, which in turn results in reduced precision. For best performance,you should use the method that was used when the indexes that you usewere generated.
How do we estimate remaining decks?
We need to divide by a number related to the number of decks remaining.But how do we obtain this number. Different players estimate the remainingcards in different manners as follows:
- Look at the shoe – This seems obviousas we are dividing by the number of remaining decks, and they are sittingin the shoe. However, this is not very accurate as all the cards arenot visible and the cards are not always stacked tightly. Very few peopleuse this method. On the other hand, Revere used to teach this methodin his private classes precisely because so few people use this methodand it doesn't require looking at the discard tray. Also, some tablesnow hide the cards in the discard tray.
- Subtract cards in discard tray –The most common method is to look at the discard tray and subtract fromthe starting number of decks. Of course this is not quite accurate forplaying decisions since it ignores the cards on the table.
- Subtract cards dealt – In calculatingthe remaining cards, subtract the total number of cards dealt from thetotal cards including those on the table both seen and unseen. Thisis a bit more accurate, and more difficult. (Many Blackjack simulatorsincorrectly use this method.)
- Subtract cards seen – Only takeinto account the actual number of cards seen. That is the cards in thediscard tray (minus unseen burn cards) plus only the cards on the tablethat you have seen. This is the most accurate and the most difficult.Few people use this method.
- Count hands – In single deck games,some people count the number of hands, multiply by 2.7 and subtractfrom 52.
By far, most people look at the discard tray.
How closely must we estimate remaining decks?
That is, what is the resolution of the estimate. Very few people estimateremaining cards to the exact card. (Although some Blackjack simulatorsinaccurately assume this.) When playing shoes, most people estimate tothe nearest remaining full-decks or half-decks remaining. When playingsingle deck, you should estimate by quarter-decks. In deeply-dealt games,you might want to be more accurate toward the end of the shoe. Alas wesee few deeply-dealt Blackjack games these days. For best results, youshould estimate the remaining decks to the same degree of accuracy thatwas used during generation of the indexes that you are using.
Custom true count calculation

Some people use a table of divisors (or multipliers) instead of dividingby the remaining decks. For example, the Mentor count uses a table ofmultipliers used to convert the running count to a true count dependingon a table of remaining decks that becomes more precise as the shoe isdepleted. This is described in Blackjack Bluebook II by Fred Renzey.

True count calculation by rounds
Yet another method is to look up a multiplier in a table based on thenumber of players and the round number. Then use that multiplier to convertthe running count to a true count. This can be used in single deck play.This is described in Play Blackjack Like the Pros by Kevin Blackwood.
How often do we calculate true counts?
Everyone recalculates before making a bet. Different players make additionalrecalculations differently as follows:
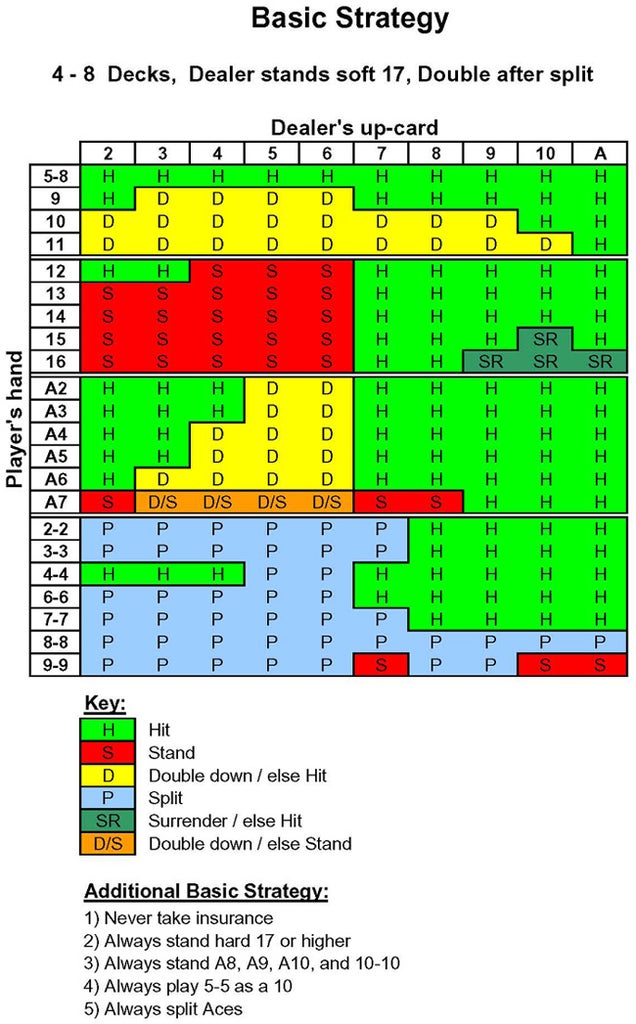
- Before Insurance – Recalculate beforean Insurance bet. Counts all seen cards, including all of your handsin face down dealing.
- Before first decision – Recalculatebefore the first playing decision in each hand.
- Before every close decision – Recalculatefor every playing decision that matters.
Recalcualtion for every decision is very important in single-deck Blackjackgames. In shoe games, failing to recalculate results in a performancehit of 5%-10% depending on penetration.
Define Counting Cards Words
Is there any time that I do not calculate true count?
What Is Considered Counting Cards
Some people use the running count for decisions with a zero index. Forexample, when you have a 16 vs. ten, the running count is actually a bitmore accurate than the true count using some strategies.
Define Counting Cards Online
And you thought it was simple.J